Oilfield & Energies
Fuelling commercial vehicles of the future 1st October 2019
By Lauren Kreno, EU Fuel Products Technical Advisor, and Dirk Pyatt, EAME Commercial Fuels Marketing Manager, at ExxonMobil
Lauren Kreno, EU Fuel Products Technical Advisor, and Dirk Pyatt, EAME Commercial Fuels Marketing Manager, at Exxon Mobil explain
Moving forward, alternatives to traditional diesel are expected to be a growing part of the commercial vehicle energy mix. While numerous alternatives fuels have been, or are in the process of being developed, the leading contenders likely to have a significant impact are biofuels, Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and electricity. These alternative fuels can be renewable depending on the source of feedstock or energy used.
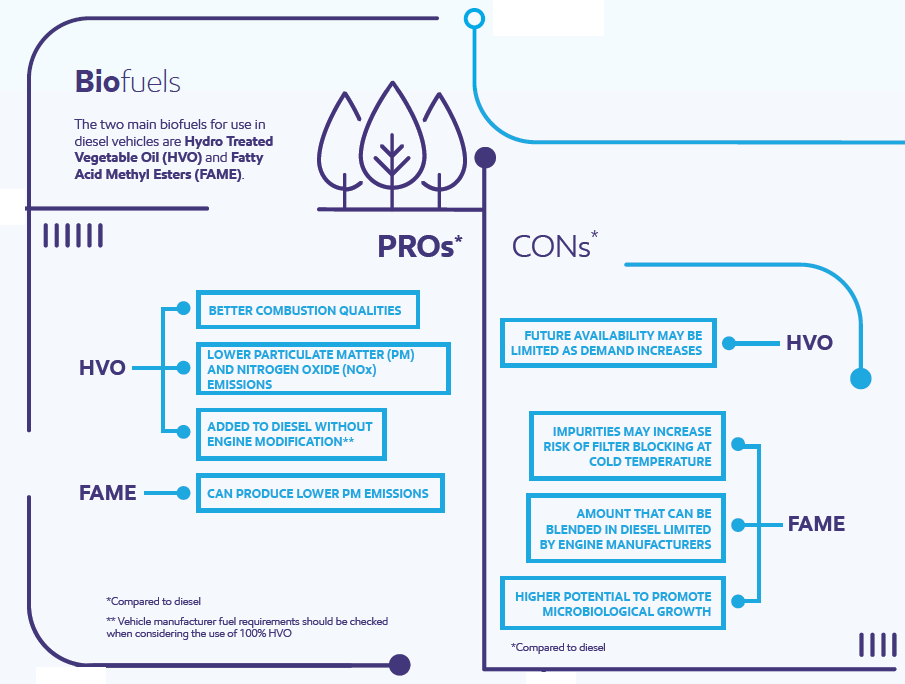
The two main biofuels for use in diesel vehicles are Hydro Treated Vegetable Oil (HVO) and Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAME).
- HVO has better combustion qualities than diesel and produces lower PM (Particulate Matter) and NOx (Nitrogen Oxide) emissions. HVO also has the advantage that it can be used as a replacement or added to traditional diesel without engine modification (vehicle manufacturer fuel requirements should be checked when considering use of 100% HVO). However, HVO availability is limited and may continue to be challenged as existing and future legislation requirements increase demand.
- FAME can produce lower PM emissions than diesel. However, it may require additional processing in order to mitigate fuel system operational issues. For example, FAME has more impurities than HVO that can cause filter blocking at lower temperatures. FAME also has a higher potential to promote microbiological growth. FAME must be blended with diesel, as engine manufacturers typically specify a maximum concentration of FAME.

- Compared the performance in heavy-duty vehicles of Esso unadditized diesel with Esso Diesel Efficient fuel
- Used third-party customer trucks (Euro III and Euro V specifications)
- Covered approximately 110,000 miles/177,000 km
- Five months of normal daily on-road operations (motorway, rural, and urban environments)
- Took trucks out of service periodically for lab testing
- Test results range of 2.1% to 3.4% lower fuel consumption.
Authors:
Lauren Kreno, EU Fuel Products Technical Advisor, and Dirk Pyatt, EAME Commercial Fuels Marketing Manager, at ExxonMobil.
Millbrook Proving Ground in the UK is one of the most comprehensive test facilities in the world for conducting independent fuels testing. Millbrook has expertise in automotive, test and propulsion technologies (ISO Certification – ISO 17025, ISO 9001 and ISO 14001).
Esso Diesel Efficient fuel claims are based on internal and third-party vehicle engine testing, laboratory testing, and/or industry or other scientific literature. Basis for comparison for all claims is versus Esso unadditized diesel. Fuel economy testing was performed in the UK using on-road trucks. Vehicle type, engine type, driving behaviour, and other factors also impact fuel and vehicle performance, emissions, and fuel economy. Esso Diesel Efficient fuel may be used in all heavy-duty and light-duty vehicles, but results may vary.
Esso Diesel Efficient is a registered trademark of Exxon Mobil Corporation or one of its subsidiaries.


